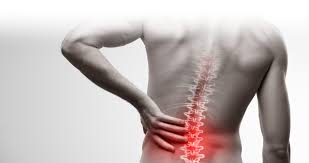
A common complaint, back pain can stem from a variety of conditions or injuries and gentle exercise program and some rest can often ease the discomfort, but persistent or severe pain requires medical attention.
Back pain: a breakdown
- Causes:
Common injuries include strains and sprains of the muscles.Degenerative Conditions : Arthritis, spinal stenosis, and herniated discs can lead to pain. Other Factors: Poor posture, obesity, and certain medical conditions can also contribute.Trauma: Back pain can also be caused by accidents, falls, and other forms of trauma
Diseases : Some types of arthritis and cancer can contribute to back pain - Types of Back Pain:
Acute: Sudden onset, lasting a few days to a few weeks.
Subacute: Pain lasting 4 to 12 weeks.
Chronic: Pain lasting longer than 12 weeks. - Symptoms:
Sharp or dull ache: The pain may radiate or be localized.
There is a feeling of stiffness, especially in the morning.
The pain worsens with movement, lifting and bending.
Numbness or tingling: In the legs or feet, potentially indicating nerve involvement.
Leg or foot weakness. - When to Seek Medical Advice:
If pain doesn’t go away after a week of at-home therapy, it’s considered severe or persistent.
Pain spreads down one or both legs, particularly if it goes below the knee.
Numbness, tingling, or weakness in one or both limbs:
Following trauma, back pain:
Severe, ongoing pain: particularly while you’re lying down or at night.
Abdominal or bowel control loss:
Inexplicable loss of weight
- Treatment:
Home Care:
Rest, ice/heat packs, over-the-counter pain relievers, and gentle exercise.
Medical Treatment:
Physical therapy, medications, injections, or surgery may be used depending on the cause and severity.